On The Diagram To The Right Movement Along The Curve From Points A To B To C Illustrates
Changes in aggregate demand cause movements along the phillips curve. In the diagram to the right point g indicates an a.
 Production Possibility Frontier Tutor2u Economics
Production Possibility Frontier Tutor2u Economics
Movement up the demand curve.
On the diagram to the right movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates. On the diagram to the right movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates reflexive marginal opportunity costs. Decreasing marginal opportunity costs. There will be a movement along the ad curve.
Rise in demand due to fall in price of the goods. There will be no change in the lras curve. On the diagram to the right movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates a.
6 on the diagram to the right movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates increasing marginal opportunity costs. For every new equilibrium point points b c and d in the aggregate graph there is a corresponding point in the phillips curve. It is also known as change in quantity demanded of that commodity.
Decreasing marginal opportunity costs. This causes the sras curve to shift to the left. The ad curve shifts to the right and there is movement upward along the sras curve.
Constant marginal opportunity costs. 7a what happens if a country produces a combination of goods that efficiently uses all of the resources available in the economy. The price of oil falls.
On the diagram to the right movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates a. Change in quantity demanded. Movement along the demand curve can be of two types.
Microeconomics chapter 2 homework. There will be no change in lras. Increasing marginal opportunity costs.
The production possibilities frontiers depicted in the diagram to the right illustrate 2. Reflexive marginal opportunity costs. This illustrates an important point.
Microeconomics chapter 2 quiz and test. Show transcribed image text on the diagram to the right a movement from a to b represents a a. The price of commodities increases by 10 this year.
The production possibilities frontiers depicted in the diagram to the right illustrate. A movement along the demand curve is caused by the change in price of the good only other things remaining constant. Decreasing marginal opportunity costs.
A curve that illustrates the demand of two goods for the average consumer.
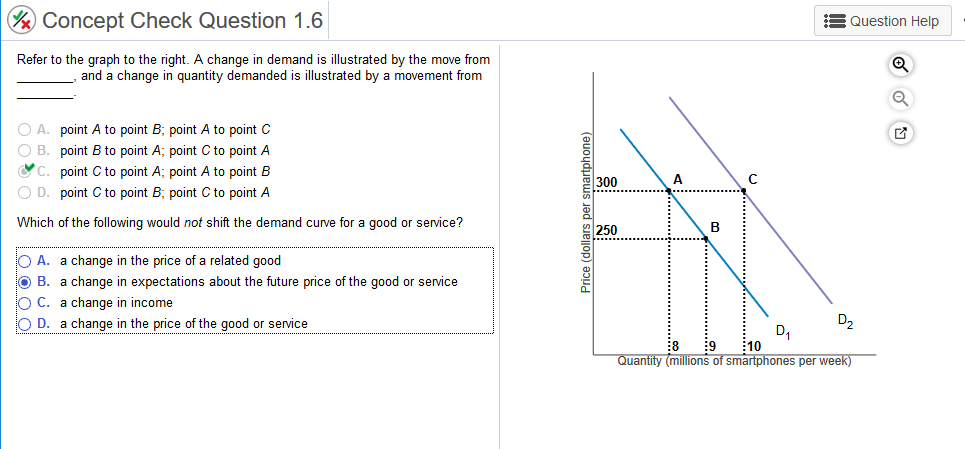
 Solved Concept Check Question 1 6 Question Help Refer To
Solved Concept Check Question 1 6 Question Help Refer To
 Econ 120 Pearson Practicehw Quizzes Flashcards Quizlet
Econ 120 Pearson Practicehw Quizzes Flashcards Quizlet
 1 Economics 101 Spring 2017 Answers To Homework 3 Due Thursday
1 Economics 101 Spring 2017 Answers To Homework 3 Due Thursday
 Shift Of The Demand Supply Curves Vs Movement Along The Demand
Shift Of The Demand Supply Curves Vs Movement Along The Demand
 Shift In Demand And Movement Along Demand Curve Economics Help
Shift In Demand And Movement Along Demand Curve Economics Help
 A Diagrammatic Representation Of The Earth S Magnetic Field
A Diagrammatic Representation Of The Earth S Magnetic Field
 Lecture Notes The Phillips Curve
Lecture Notes The Phillips Curve
 4 1 Demand And Supply At Work In Labor Markets Principles Of Economics
4 1 Demand And Supply At Work In Labor Markets Principles Of Economics
 Econ 120 Pearson Practicehw Quizzes Flashcards Quizlet
Econ 120 Pearson Practicehw Quizzes Flashcards Quizlet
 Econ 120 Pearson Practicehw Quizzes Flashcards Quizlet
Econ 120 Pearson Practicehw Quizzes Flashcards Quizlet
 3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of Microeconomics
3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of Microeconomics
 Law Of Supply And Demand Basic Economics
Law Of Supply And Demand Basic Economics
 Understanding Subsidy Benefit Cost And Market Effect
Understanding Subsidy Benefit Cost And Market Effect
 Shift Of The Demand Supply Curves Vs Movement Along The Demand
Shift Of The Demand Supply Curves Vs Movement Along The Demand
 Mechanics Physics Britannica Com
Mechanics Physics Britannica Com
 Ship Stability Understanding Curves Of Static Stability
Ship Stability Understanding Curves Of Static Stability
 Understanding Flight Zone And Point Of Balance For Low Stress
Understanding Flight Zone And Point Of Balance For Low Stress
 Price Elasticity Of Demand 2 0 Where Theory Meets Application Toptal
Price Elasticity Of Demand 2 0 Where Theory Meets Application Toptal

0 Response to "On The Diagram To The Right Movement Along The Curve From Points A To B To C Illustrates"
Post a Comment