Given The Cost Curves In The Diagram What Market Situation Would You Expect To Occur
Question a firm can be the sole supplier of a good and sill not be considered a monopoly if. Is the same as the industry demand curve.
Is the same as a price taking firm.

Given the cost curves in the diagram what market situation would you expect to occur. Tool identify the output and price that would occur if this was a perfectly competitive market. The market price is equal to 30. Question 10 in the graph the profit maximizing price for a monopoly is.
In a competitive market we expect firms to compete with each other until the point where marginal cost increases to match the demand curve at the equilibrium point. Marginal revenue for a monopolist is a. Question 8 given the cost curves in the diagram what market situation would you expect to occur.
Horizontal just like for the perfectly competitive firm. 2 using the point drawing. Likewise the supply curve is the marginal cost curve and represents the marginal costs at each quantity level.
The monopolist must choose the profit maximizing price output combination the output at which revenue equals cost and the highest price possible as given by the curve for that particular output rate. Downward sloping and always equal to price. Micro eco chapter 23 24 25.
The demand curve of the monopolist a. Question 11 the demand curve faced by the monopolist. What would you expect to be the pattern of international specialization and trade.
Consider a situation similar to that in figure in which two countries that can produce a good are subject to forward falling supply curves. Consider the short run cost curve shown on the graph. You also know that the market demand for this product is given by the equation p 1000 2q where q is the market quantity.
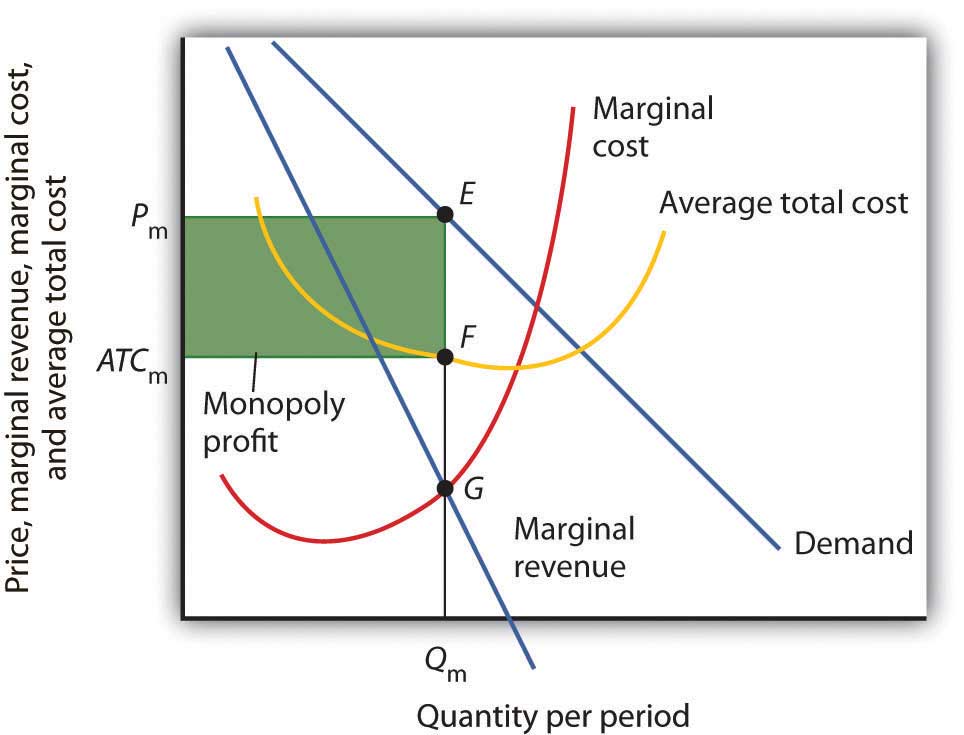
With our total benefits blue and our total costs red we can easily determine our total market surplus is the green area in figure 36j below. In addition you are told that the market supply curve is given by the equation p 100 q. A monopolists demand marginal revenue and marginal cost curves are shown in the diagram to the right.
For this situation to be able to occur we make the assumption of upward sloping supply marginal cost curves. Given the cost curves in the diagram what market situation would you expect to occur. Find and shade in the area of the deadweight loss due to monopoly power in this market.
The area under the marginal cost curve represents our total market costs. The u shaped curve is perfectly competitive firms short run average variable cost curve and the upward sloping curve is its marginal cost curve. In this case however suppose the two countries have the same costs so that their supply curves are identical.
Question 9 a firm can be the sole supplier of a good and sill not be considered a monopoly if.
 The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive

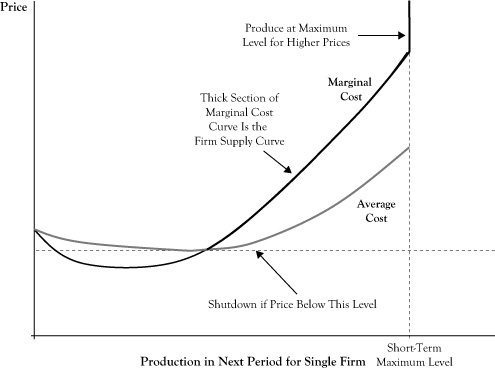 Market Equilibrium And The Perfect Competition Model
Market Equilibrium And The Perfect Competition Model

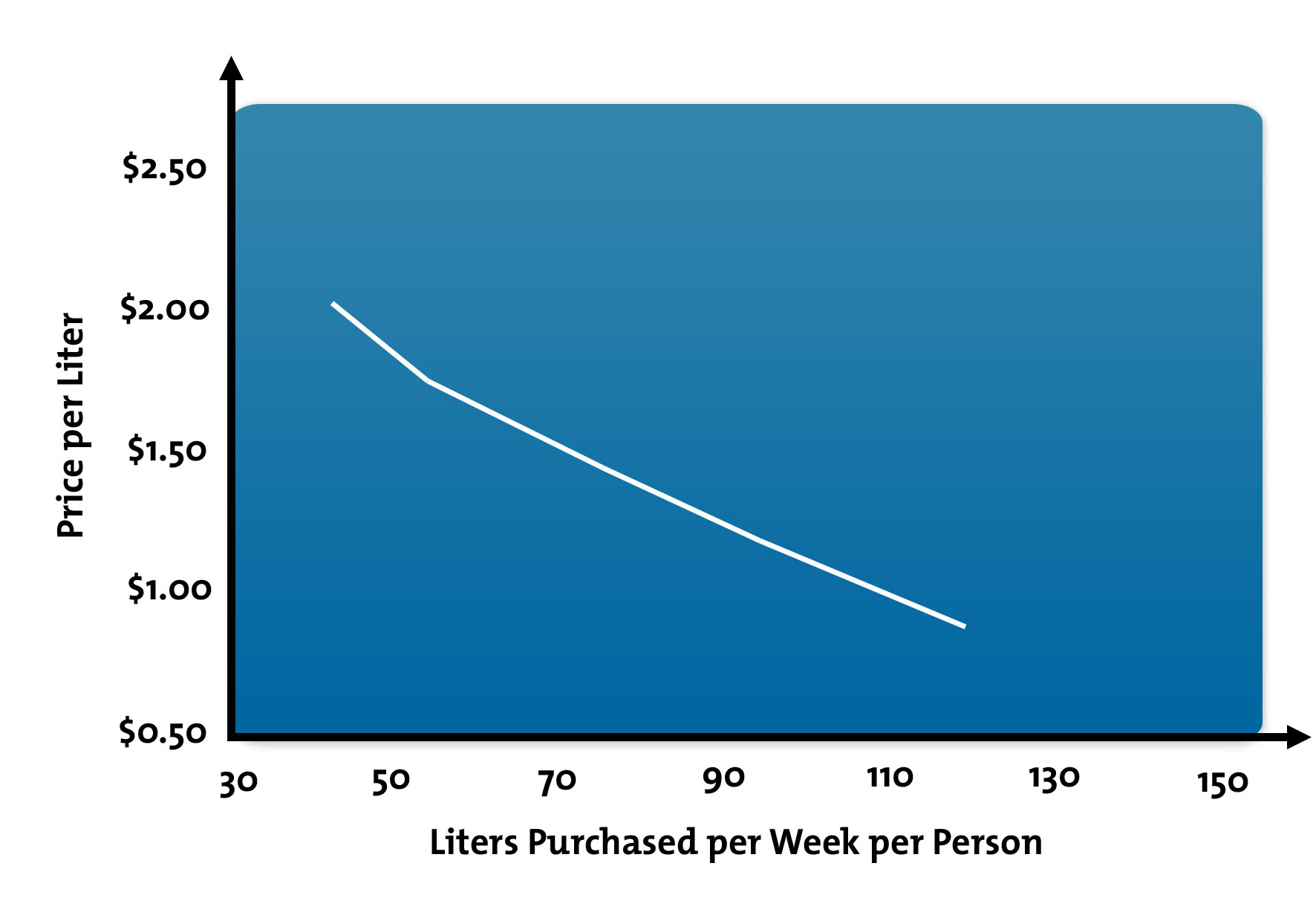 What Are Supply And Demand Curves From Mindtools Com
What Are Supply And Demand Curves From Mindtools Com
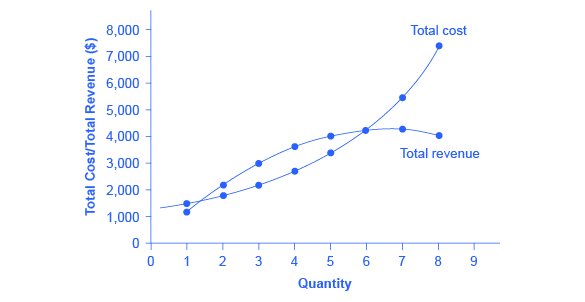 9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price
9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price
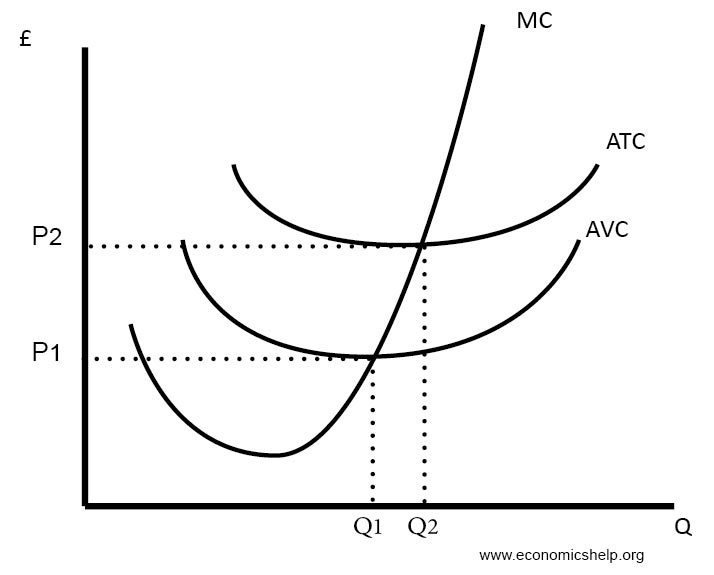 Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
 Break Even Economics Wikipedia
Break Even Economics Wikipedia
 Solved 9 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram S
Solved 9 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram S
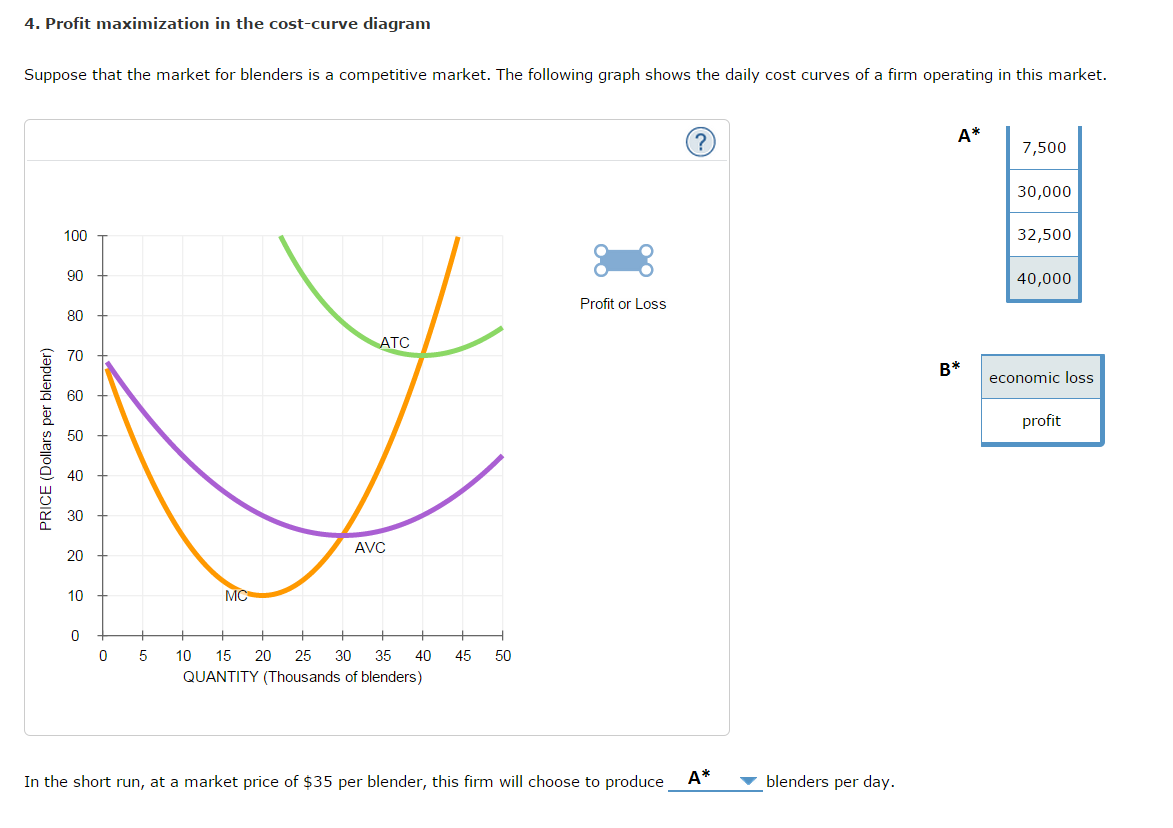 Solved Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Supp
Solved Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Supp

 Economy Society And Public Policy Unit 7 Firms And Markets For
Economy Society And Public Policy Unit 7 Firms And Markets For
 A Good Introductory Micro Text That Deals With These Issues Is Paul
A Good Introductory Micro Text That Deals With These Issues Is Paul
 Solved 3 Perfect Competition Market Total 8 Points A
Solved 3 Perfect Competition Market Total 8 Points A
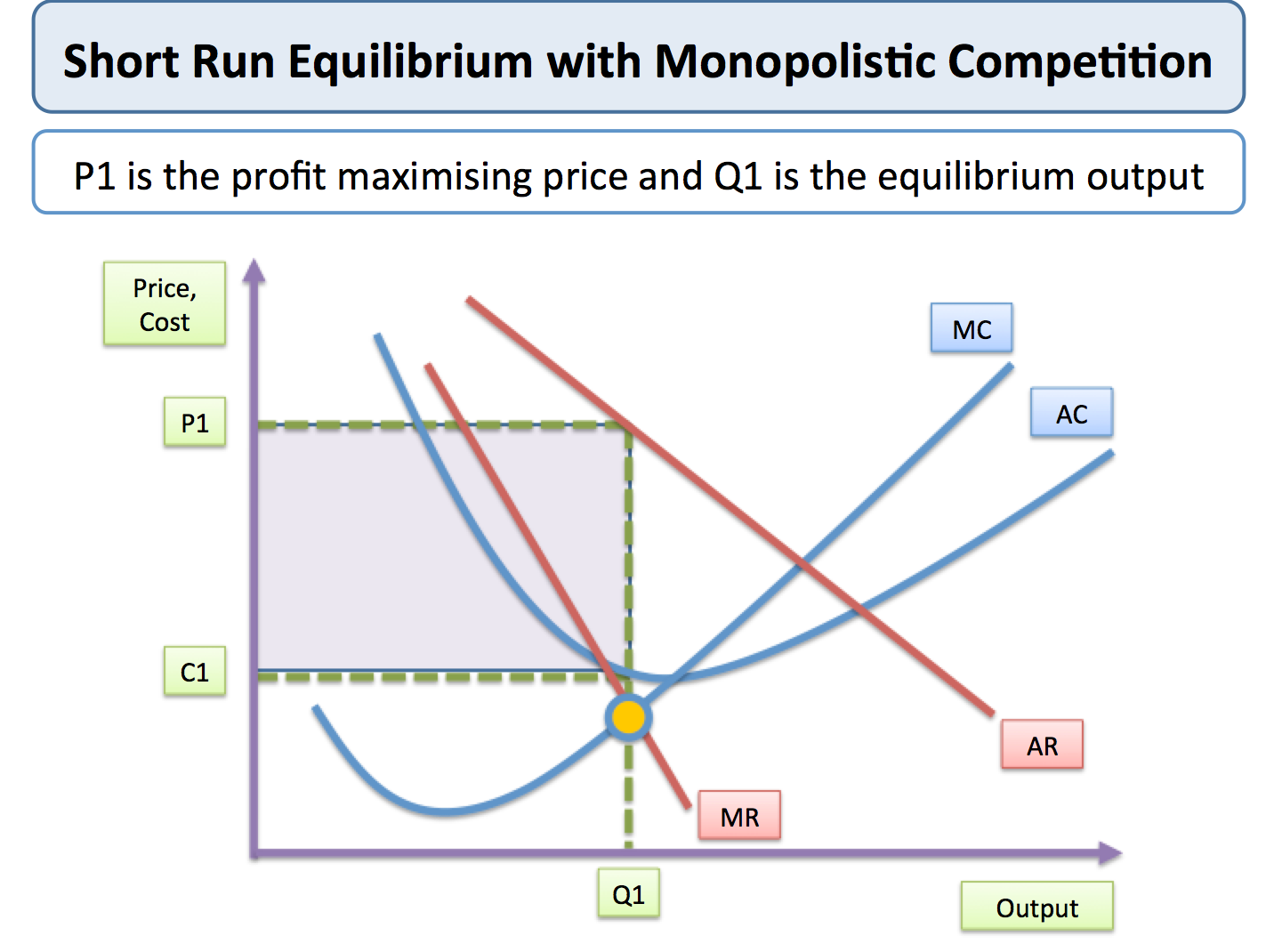 Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics
Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics
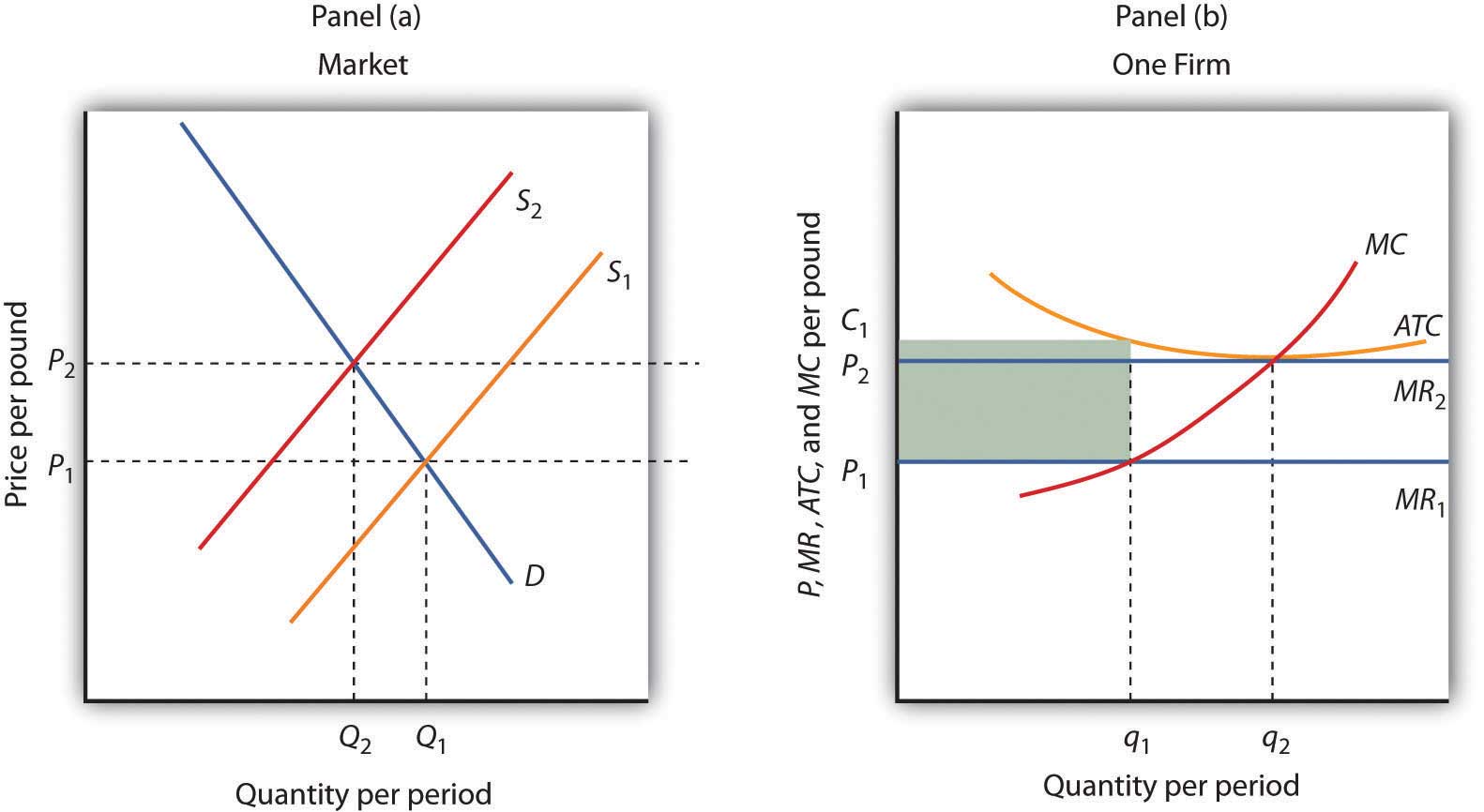 Perfect Competition In The Long Run
Perfect Competition In The Long Run




0 Response to "Given The Cost Curves In The Diagram What Market Situation Would You Expect To Occur"
Post a Comment