Refer To The Diagram Diseconomies Of Scale
5 the government of southland wants to improve resource allocation in the country. The firms long run atc curve will be rising.
 Diseconomies Of Scale Economics Online
Diseconomies Of Scale Economics Online
Marginal cost intersects average total cost.

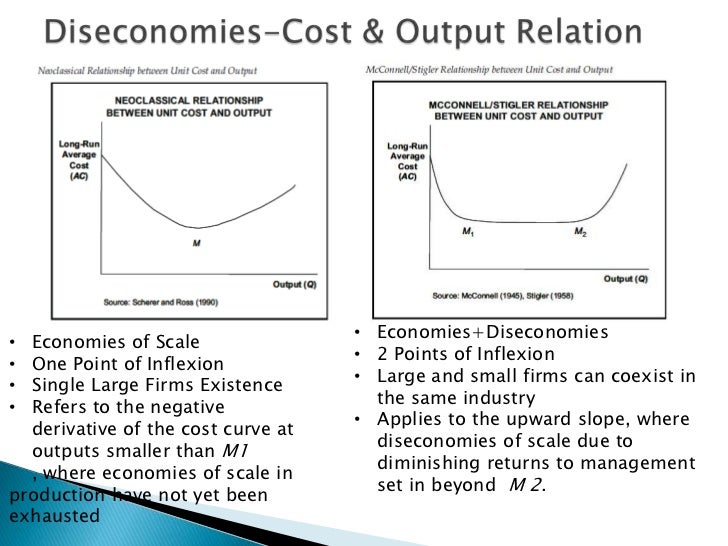
Refer to the diagram diseconomies of scale. Cbegin at output q3. The long run average total cost curve falls. These diseconomies arise due to the use of unskilled labourers outdated methods of production etc.
Refer to the above data. It is encountering diseconomies of scale. With this principle rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output a firm sees an increase in marginal costs when output is increased.
The greater the quantity of output produced the lower the per unit fixed cost. Refer to the above information the marginal cost of. Refer to the above data.
The law of diminishing returns is taking hold. Co operation workers in large firms may develop a sense of alienation and loss of morale. Diseconomies of scale happen when a company or business grows so large that the costs per unit increase.
The average variable cost of 4 units of output is. It is encountering economies of scale. Larger firms are able to raise finance for new investment.
Reduce the size of the business by closing factories shops and offices that making workers unemployed. The total output of this firm will cease to expand. Dare in evidence at all output levels.
Abegin at output q1. Refer to the diagram. Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of outputthe advantage arises due to the inverse relationship between per unit fixed cost and the quantity produced.
It takes place when economies of scale no longer function for a firm. Diseconomies of scale of production. Achieving efficient flows of information in large businesses is expensive as is the cost of managing supply contracts with hundreds of suppliers at different points of an industrys supply chain.
If a labor force in excess of q3 is employed. Refer to the diagram where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. Solution for diseconomies of scale.
The word diseconomies refer to all those losses which accrue to the firms in the industry due to the expansion of their output to a certain limit. Boccur over the q1q3 range of output. If a firm increases all of its inputs by 10 percent and its output increases by 15 percent then.
Split the business up into a number of smaller businesses each with their own managers workers. When diseconomies of scale occur.
Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale
 Solved 1 Refer To Graph A The Difference Between The Sra
Solved 1 Refer To Graph A The Difference Between The Sra
Internal Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale Meaning And Types
/economies-of-scale-3305926-FINAL-5bc4bf7ac9e77c00528fcecf.png) Economies Of Scale Definition Types
Economies Of Scale Definition Types
 Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale
Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale
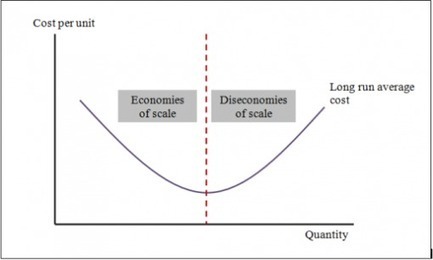
 Explaining Natural Monopoly Tutor2u Economics
Explaining Natural Monopoly Tutor2u Economics
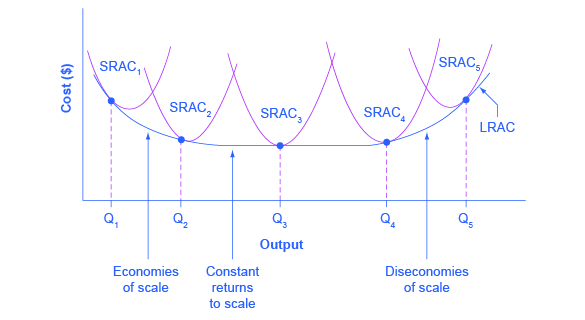
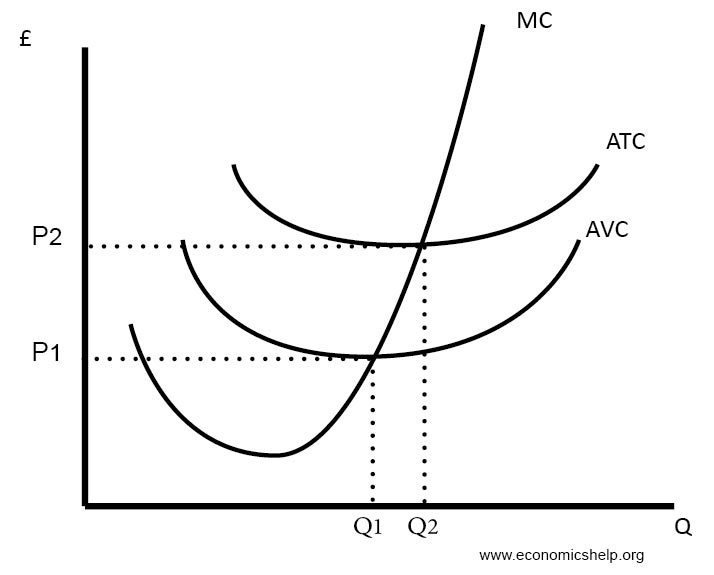 Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
 Economies Of Scale Tutor2u Business
Economies Of Scale Tutor2u Business
 Refer To The Above Diagram Diseconomies Of Scale A Begin At Output Q
Refer To The Above Diagram Diseconomies Of Scale A Begin At Output Q
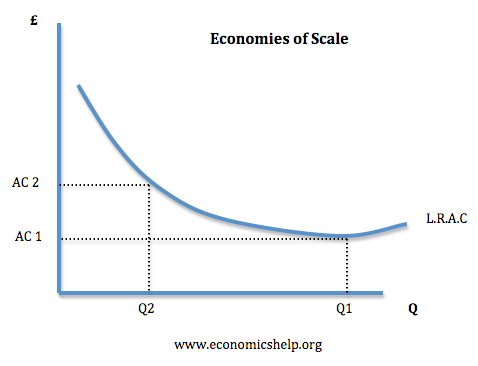 Pros And Cons Of Mergers Economics Help
Pros And Cons Of Mergers Economics Help
 Economies Of Scale Intelligent Economist
Economies Of Scale Intelligent Economist
Internal Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale Meaning And Types
 Economies And Dis Economies Of Scale In Water And Sanitation Systems
Economies And Dis Economies Of Scale In Water And Sanitation Systems
 Conflicts Between Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale Increasing
Conflicts Between Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale Increasing
 Economies Diseconomies Of Scale
Economies Diseconomies Of Scale
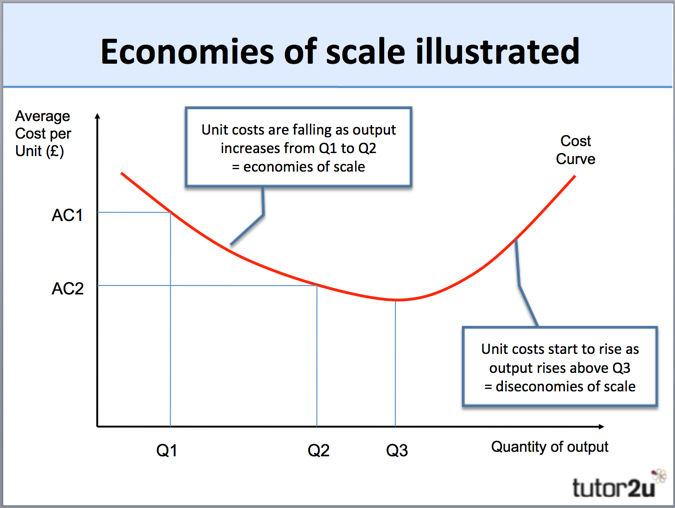 Economies Of Scale Tutor2u Business
Economies Of Scale Tutor2u Business
 Diseconomies Of Scale Effect On Effort Equation 12 Defines The
Diseconomies Of Scale Effect On Effort Equation 12 Defines The

 Visual Identification Of Outliers With Diseconomies Of Scale
Visual Identification Of Outliers With Diseconomies Of Scale
0 Response to "Refer To The Diagram Diseconomies Of Scale"
Post a Comment