Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell
This is an animal cell. Follow these diagrams to study more about the structures of the cells and well start by giving you the first diagram below.
Ostrich egg is the largest eukaryotic cell known measuring 170 mm x150 mm.

Diagram of a eukaryotic cell. Due to the lack of a cell wall animal cells can adopt a variety of shapes. To help you remember prokaryotes parts and pieces. While both animal and plant cells have microtubule organizing centers mtocs.
The cells of plants algae and fungi have thick protective cell walls which provide support help maintain the shape of the cell and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting. All animals are eukaryotic. In eukaryotic cells the cytoskeleton is composed mainly of three types of filaments.
Animal cells versus plant cells. However there are some striking differences between animal and plant cells. The gel like substance that surrounds all the organelles in the cell is called cytosol.
Animal cells are distinct from those of other eukaryotes most notably plants as they lack cell walls and chloroplasts and have smaller vacuoles. A phagocytic cell can even engulf other structures. Like eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm a gel like substance that makes up the filling of the cell and a cytoskeleton that holds components of the cell in place.
The eukaryotic cells are too complex than prokaryotic cells and evolved from them about 15 billion years ago bya. Its a relatively recent scientific discovery that rod shaped bacteria and archaea possess cytoskeletal proteins that function similarly to the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. Each eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane cytoplasm a nucleus ribosomes mitochondria peroxisomes and in some vacuoles.
All cells both prokaryotic and eukaryotic have a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cell envelope external structures. Prokaryotic cell diagrams are available in this page providing you with clear diagrams of the prokaryotic cell and its difference with eukaryotic cell.
The nuclei are delimited by nuclear membranes and contain nucleoli and more than one chromosome made up of dna and histones. Microtubules microfilaments and intermediate filaments. The figure below shows the structure of a eukaryotic cell.
Structure of eukaryotic cells with diagram these systems are incapable of internal movement and contain in addition a number of energy transducing systems such as mitotic apparatus multi stranded flagella and so on. Eukaryotic cell size varies greatly from 10 mm to 500 mm.
 Animal Cell Cross Section Structure Of A Eukaryotic Cell Vector
Animal Cell Cross Section Structure Of A Eukaryotic Cell Vector
Structure Of Eukaryotic Cells With Diagram

 Cell Biology Types Of Cells Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Cell Biology Types Of Cells Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
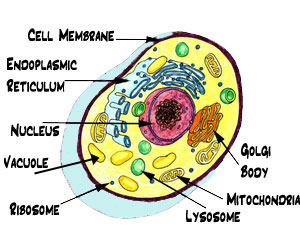 What Are Eukaryotes Cell Biology Quatr Us Study Guides
What Are Eukaryotes Cell Biology Quatr Us Study Guides
Eukaryotic Cells Definition Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Parts
 Cell Labeling Worksheet Unique Bacterial Cell Diagram Eukaryotic
Cell Labeling Worksheet Unique Bacterial Cell Diagram Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Blank Simple Animal Cell Diagram Related

 Eukaryotic Cells Lo To Be Able To Label A Diagram Of A Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cells Lo To Be Able To Label A Diagram Of A Eukaryotic
 Plant Cell Anatomy Cross Section Structure Stock Vector Royalty
Plant Cell Anatomy Cross Section Structure Stock Vector Royalty
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Venn Diagram Diagram Eukaryote Cell
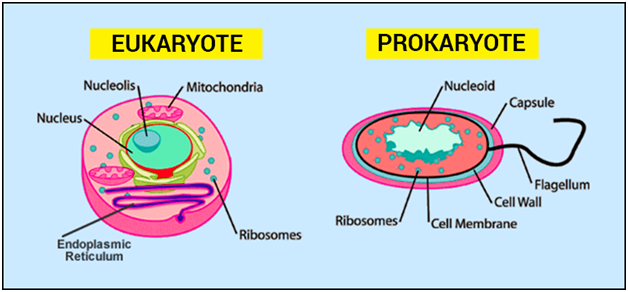 Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Comparison And Differences
Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Comparison And Differences
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Sciencetopia
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Sciencetopia
 Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet 37 New Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic
Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet 37 New Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic
 Images Of Venn Diagram Comparing Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Images Of Venn Diagram Comparing Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Eukaryote Cell Download Cell
 5 Plan Diagrams Of Tissue And Organ Prokaryotic And Eukariotic Cells
5 Plan Diagrams Of Tissue And Organ Prokaryotic And Eukariotic Cells
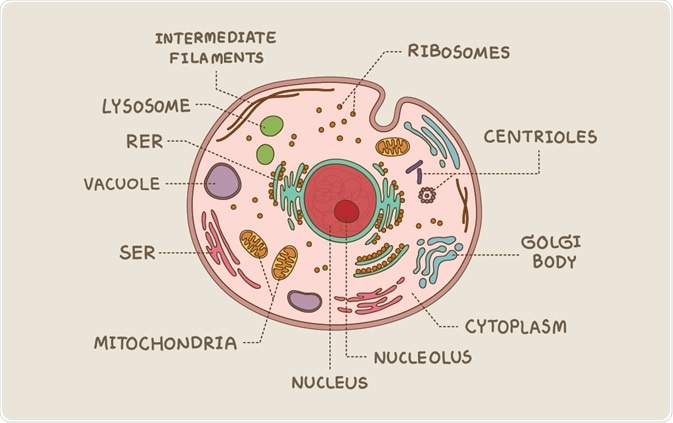 Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells Similarities And Differences
Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells Similarities And Differences
0 Response to "Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell"
Post a Comment