Complete The Free Body Diagram By Adding The Forces That Act On The Skier
Each force arrow in the diagram is labeled to indicate the exact type of force. A free body diagram makes solving newtons second law for a given situation easier because youre modeling the system as something simpler than it actually is.
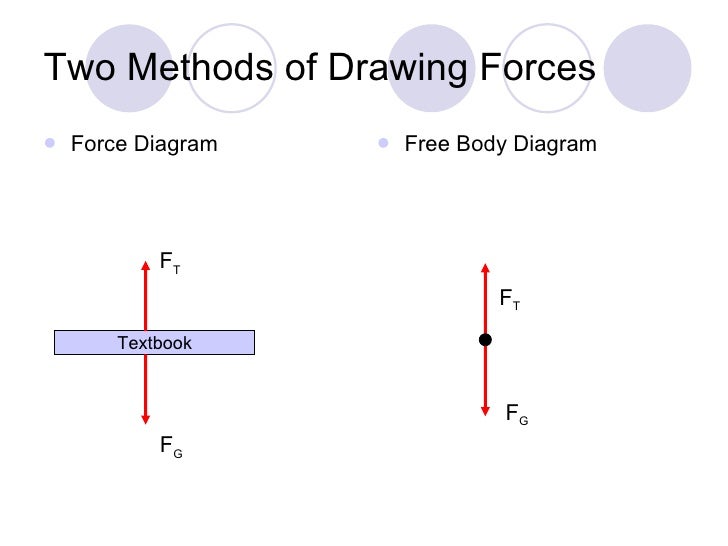
Forces And Free Body Diagrams Ppt Video Online Download
Bcomplete the chairs free body diagram by adding the forces that act on it.
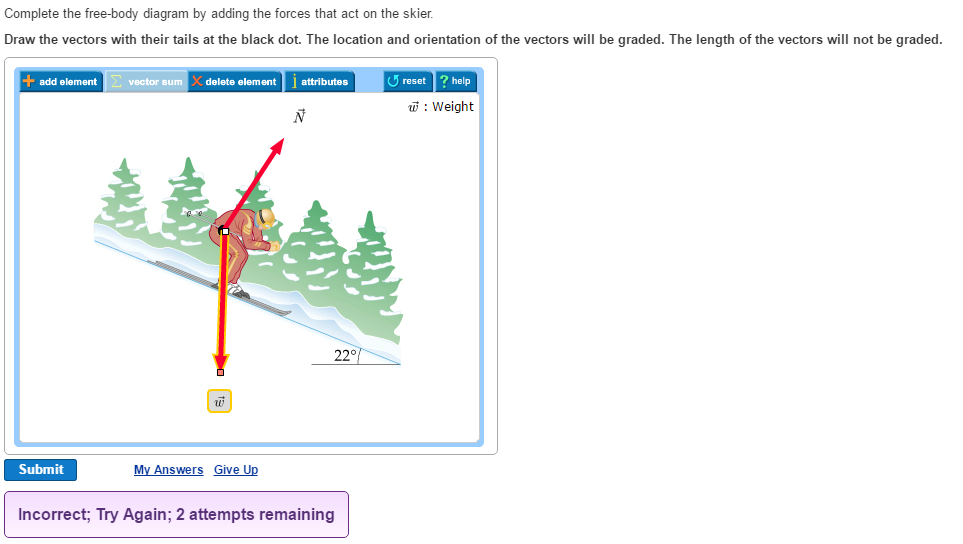
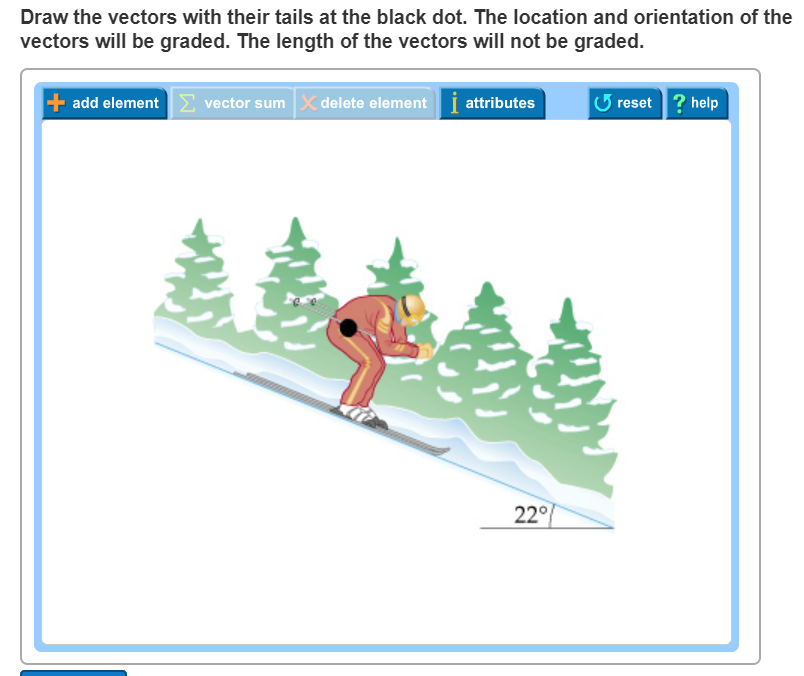
Complete the free body diagram by adding the forces that act on the skier. The free body diagram of figure 63a the force resulting from normal contact at a is represented by f. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. Draw the vectors with their tails at the black dot.
Normal force is present to counteract the effect of the skiers weight on the ski slope following newtons third law. The surface is smooth and inclined at an angle of 22 with the horizontal. Physics 151 notes for online lecture 22 a free body diagram is a way to represent all of the forces that act on a body.
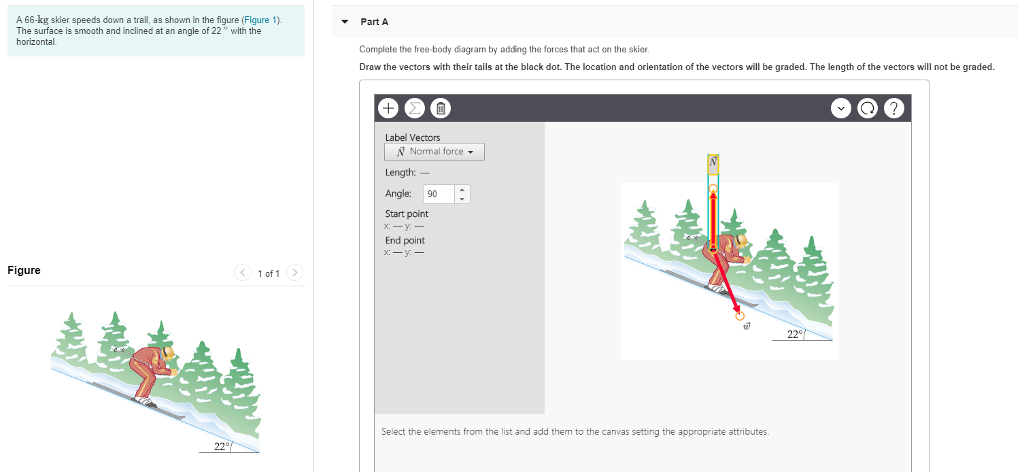
Determine the magnitude of the normal force acting on the skier. The line of action of the force is along the cable. A 62 skier speeds down a trail as shown in the figure.
1 answer below. To draw a free body diagram. A complete the childs free body diagram by adding the forces that act on the child.
Draw the vectors with their tails at the black dot. A 89 kg child sits in a 35 kg high chair a complete the childs free body diagram by adding the f. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting.
A 89 kg child sits in a 35 kg high chair. Part a complete the childs freebody diagram by adding the forces that act on the child. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded.
At point b cable. Complete the free body diagram by adding the forces that act on the skier. The surface is smooth and inclined at an angle of θ 21 with the horizontal.
Water skiers start with their tips out of the water so that when the boat starts pulling they can push against the water to lift themselves up. The force that lifts the skier isnt buoyancy its the reaction force from the angled skis pushing water down. We know its direction is normal to the surface so as to push on the system.
Once on top of the water they still hold their skis at a slight angle. At this support a force acts on the system. The vectors are for w weight and n normal force.
Weight is present presumably because gravity is pulling the skier down. The exact length of the vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. A complete the free body diagram by adding the forces that act on the skier.
Draw the vectors with their tails at the black dot. Normal force kinetic friction and weight. It is generally customary in a free body diagram to represent the object by a box and to draw the force arrow from the center of the box outward in the direction.
A 61 kg skier speeds down a trail as shown in figure 5 24.
 Solved A 60 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
Solved A 60 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
 Snow Reaction Force The Skier S Manifesto
Snow Reaction Force The Skier S Manifesto
When To Use Cos Or Sin In Physics Problems Physics Forums
5 4 Inclined Planes Texas Gateway
Chapter 4 Dynamics Force And Newton S Laws Of Motion
 Step Two Identify All Forces Acting On The Object Free Body Diagram
Step Two Identify All Forces Acting On The Object Free Body Diagram
 Dynamics The Laws Of Motion Ppt Download
Dynamics The Laws Of Motion Ppt Download
 Solved A 64 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
Solved A 64 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
Inclined Planes Problems With Solutions
 Openstax College Physics Ch4 Dynamics Force And Newton S Laws
Openstax College Physics Ch4 Dynamics Force And Newton S Laws
 Solved A 66 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
Solved A 66 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
 Homework And Exercises Finding The Free Body Force Diagram Of This
Homework And Exercises Finding The Free Body Force Diagram Of This
A Kinematic And Kinetic Study Of Alpine Skiing Technique In Slalom Pdf
 Solved A 64 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
Solved A 64 Kg Skier Speeds Down A Trail As Shown In The
Physics 151 Notes For Online Lecture 2 2
Flow Visualisation Of Downhill Skiers Using The Lattice Boltzmann
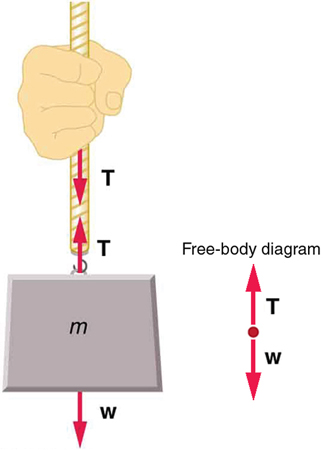 Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces College Physics
Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces College Physics

0 Response to "Complete The Free Body Diagram By Adding The Forces That Act On The Skier"
Post a Comment