Refer To The Diagram To The Right The Deadweight Loss Due To A Monopoly Is Represented By The Area
Refer to figure 5 2 the deadweight loss due to the. Cannot be determined from the diagram.
At the profit maximizing quantity what is the difference between the monopoly ʹ s price and the marginal cost of production.
Refer to the diagram to the right the deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist. Deadweight loss deadweight loss is the lost welfare because of a market failure or intervention. The monopoly must lower its price to sell more of its product.
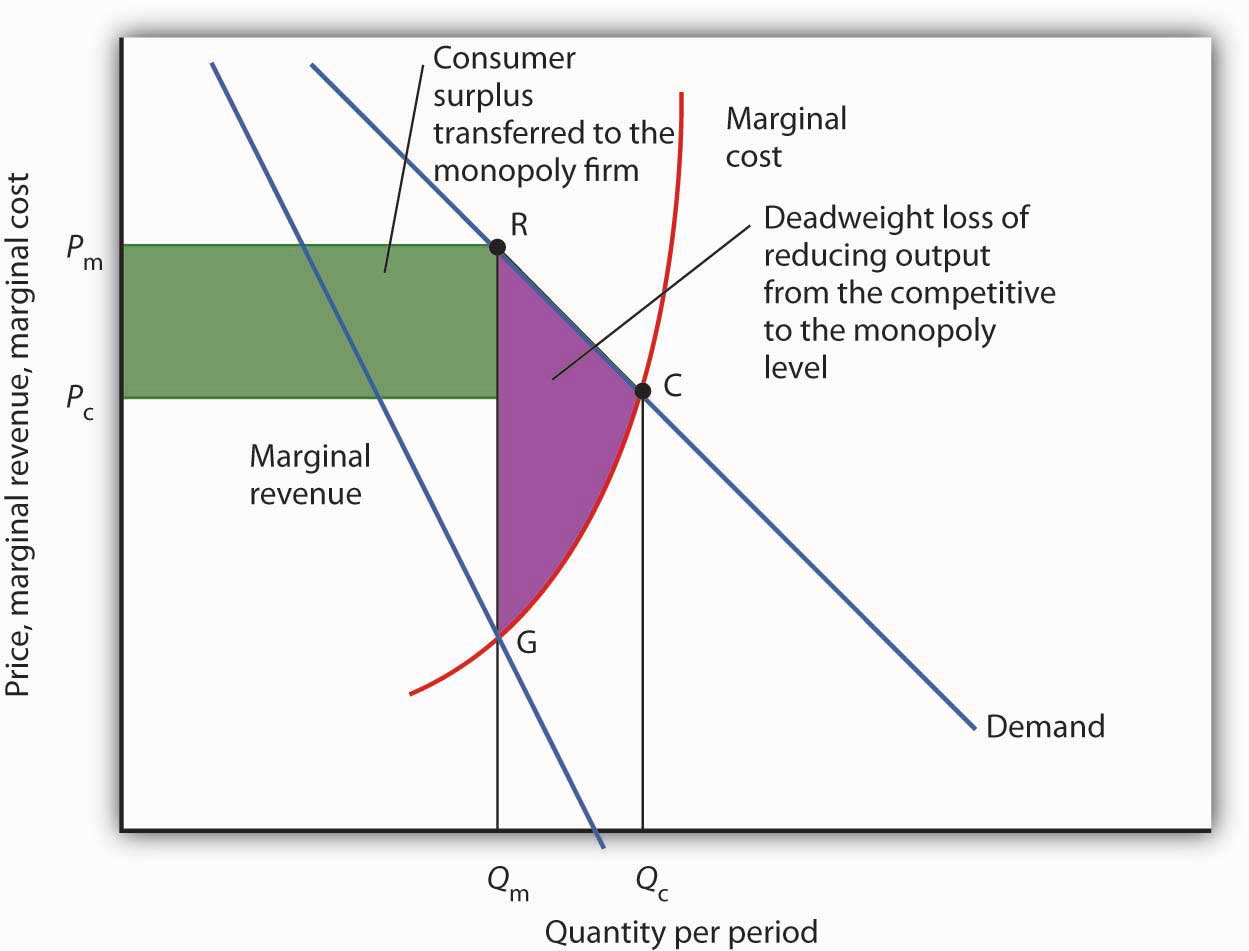
Refer to the figure above. That is the potential gain from moving to the efficient solution. The area grc is a deadweight loss.
A 8 b 1150 c 21 d there is no difference. Higher prices higher price and lower output than under perfect competition. Refer to the figure above.
Relative to a perfectly competitive market a monopoly results in a gain in producer surplus equal to the gain in consumer surplus. The deadweight loss caused by a profit maximizing monopoly amounts to a. In the area of the deadweight loss due to monopoly power in this market.
A monopolists demand marginal revenue and marginal cost curves are shown in the diagram to the right. Disadvantages of a monopoly. In this case it is caused because the monopolist will set a price higher than the marginal cost.
The monopolists maximum producer surplus a. Cannot be determined from the diagram. Refer to figure 14 6.
Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram to the right produces positive output. Refer to figure 5 2 the deadweight loss due to the externality is represented from econ 201 at university of oregon. This means there will be people willing to pay more than the cost of production which will not be able to purchase.
This leads to a decline in consumer surplus and a deadweight welfare loss allocative inefficiency. The deadweight loss due to the externality is represented by the area a abc. Mr marginal revenue curve mc marginal cost curve dwl deadweight loss associated with monopoly in the case of perfect.
A monopoly is allocatively inefficient because in monopoly the price is greater than mc. It is the shaded area grc. 1 using the point drawing.
Subtracting this cost from the benefit gives us the net gain of moving from the monopoly to the competitive solution. The deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area a fq1q2e. A gain in producer surplus equal to the loss in consumer surplus.
Monopoly In A Perfectly Competitive Market With Diagram
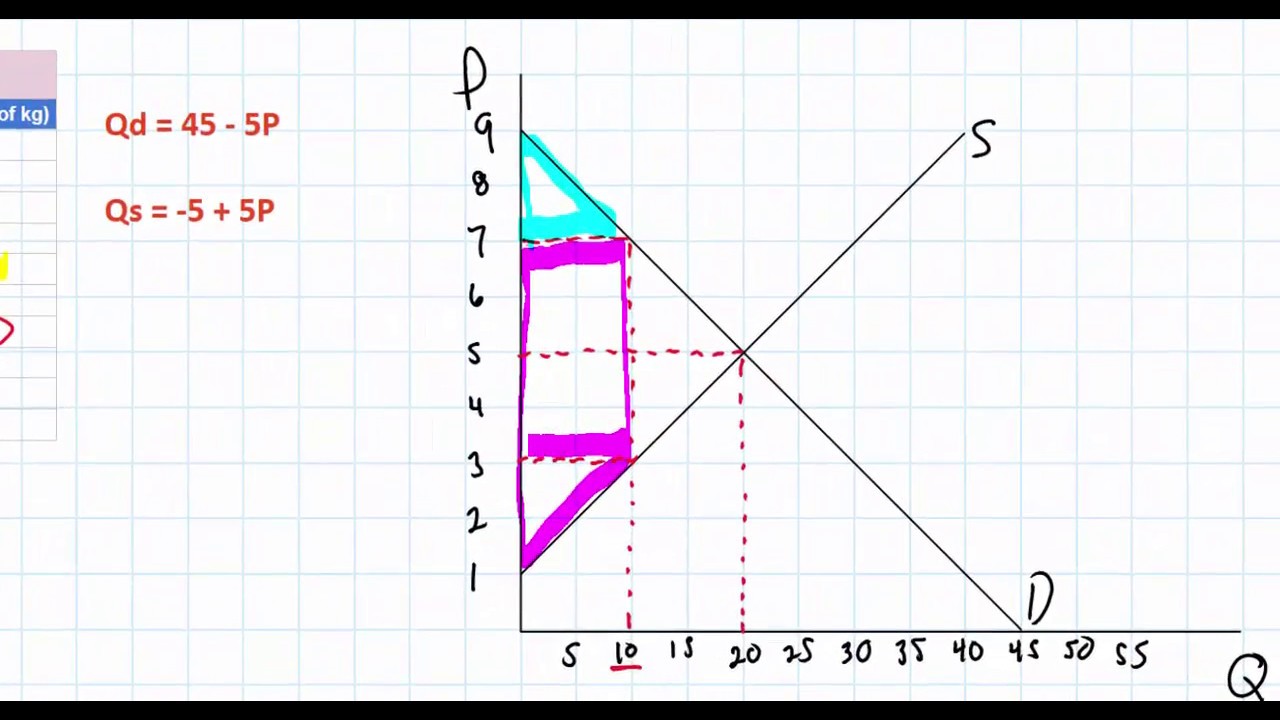 Calculating The Area Of Deadweight Loss Welfare Loss In A Linear
Calculating The Area Of Deadweight Loss Welfare Loss In A Linear
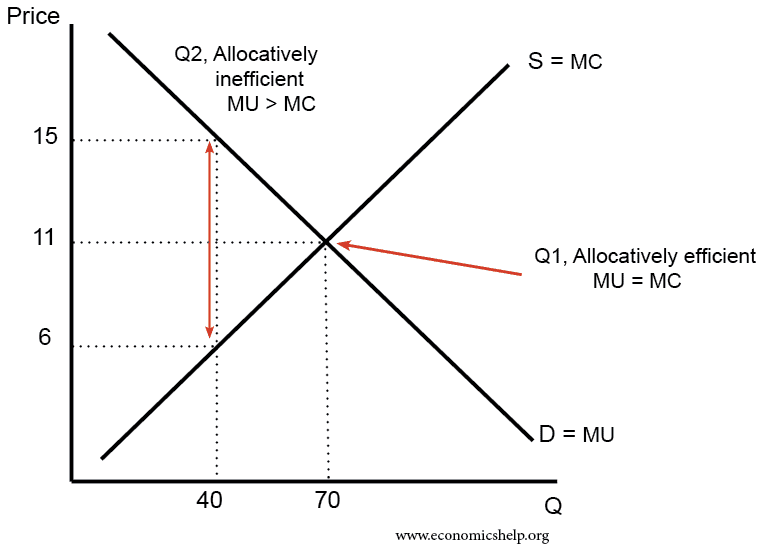 Allocative Efficiency Economics Help
Allocative Efficiency Economics Help
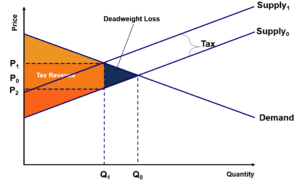 Deadweight Loss Examples How To Calculate Deadweight Loss
Deadweight Loss Examples How To Calculate Deadweight Loss
 Facebook And The Cost Of Monopoly Stratechery By Ben Thompson
Facebook And The Cost Of Monopoly Stratechery By Ben Thompson
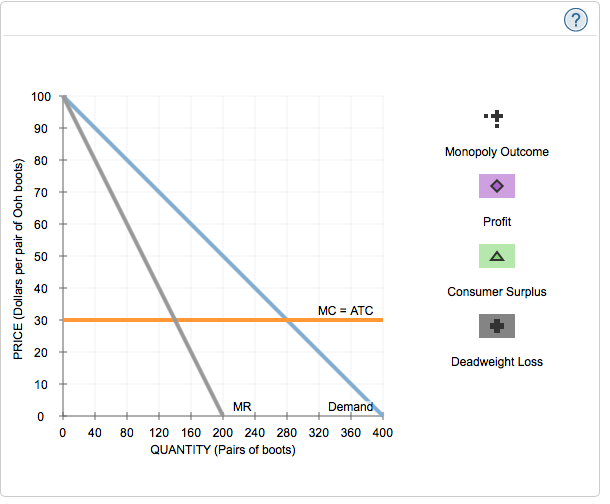 Solved 7 Price Discrimination And Welfare Suppose Barefe
Solved 7 Price Discrimination And Welfare Suppose Barefe
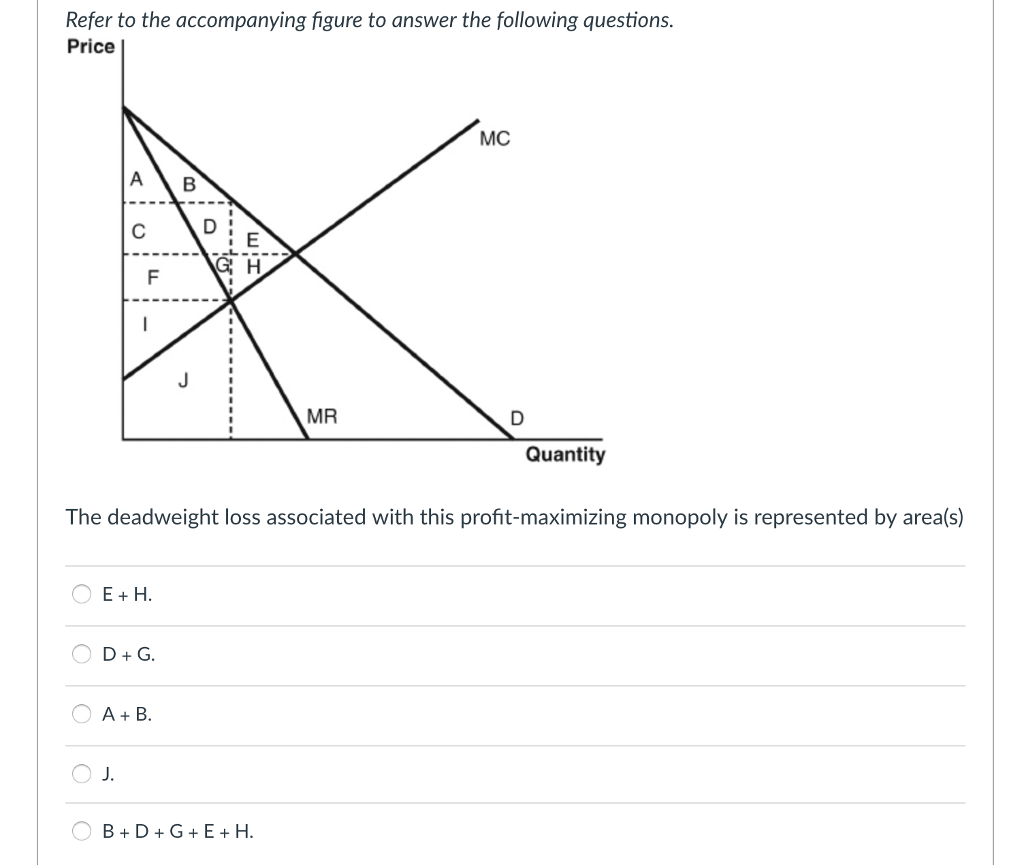 Solved Refer To The Accompanying Figure To Answer The Fol
Solved Refer To The Accompanying Figure To Answer The Fol
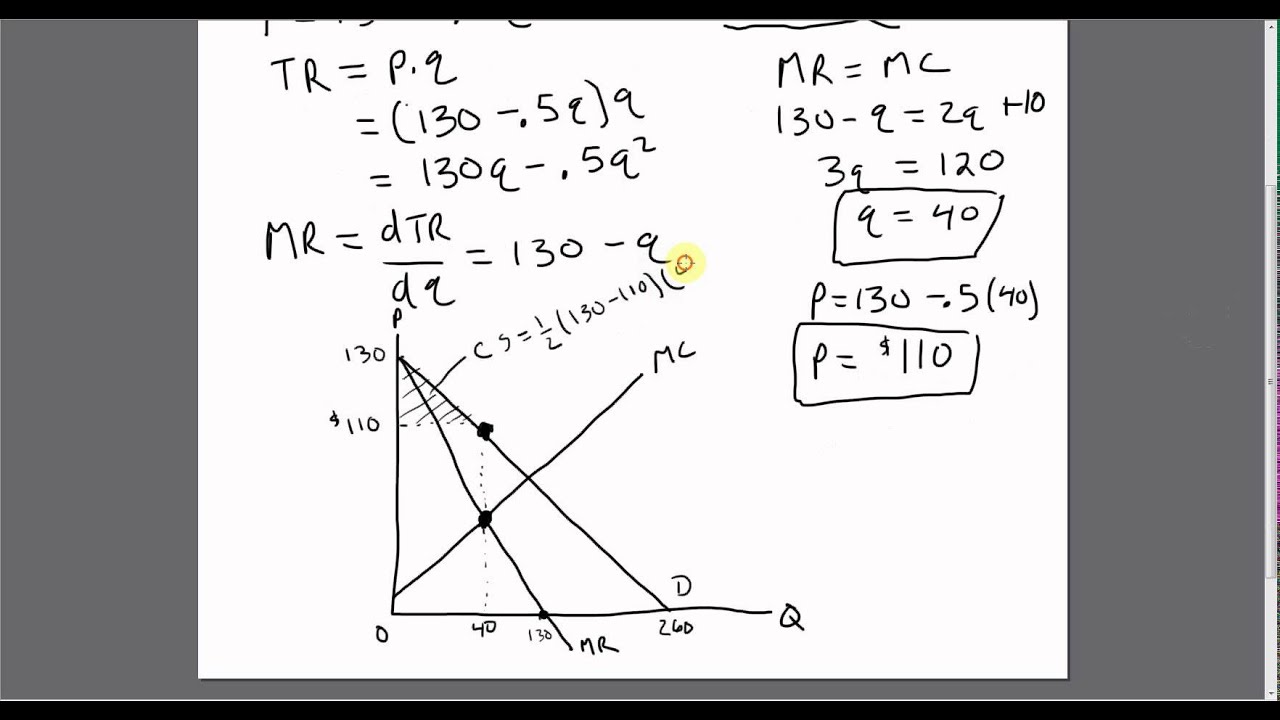 Monopoly Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Deadweight Loss Youtube
Monopoly Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Deadweight Loss Youtube
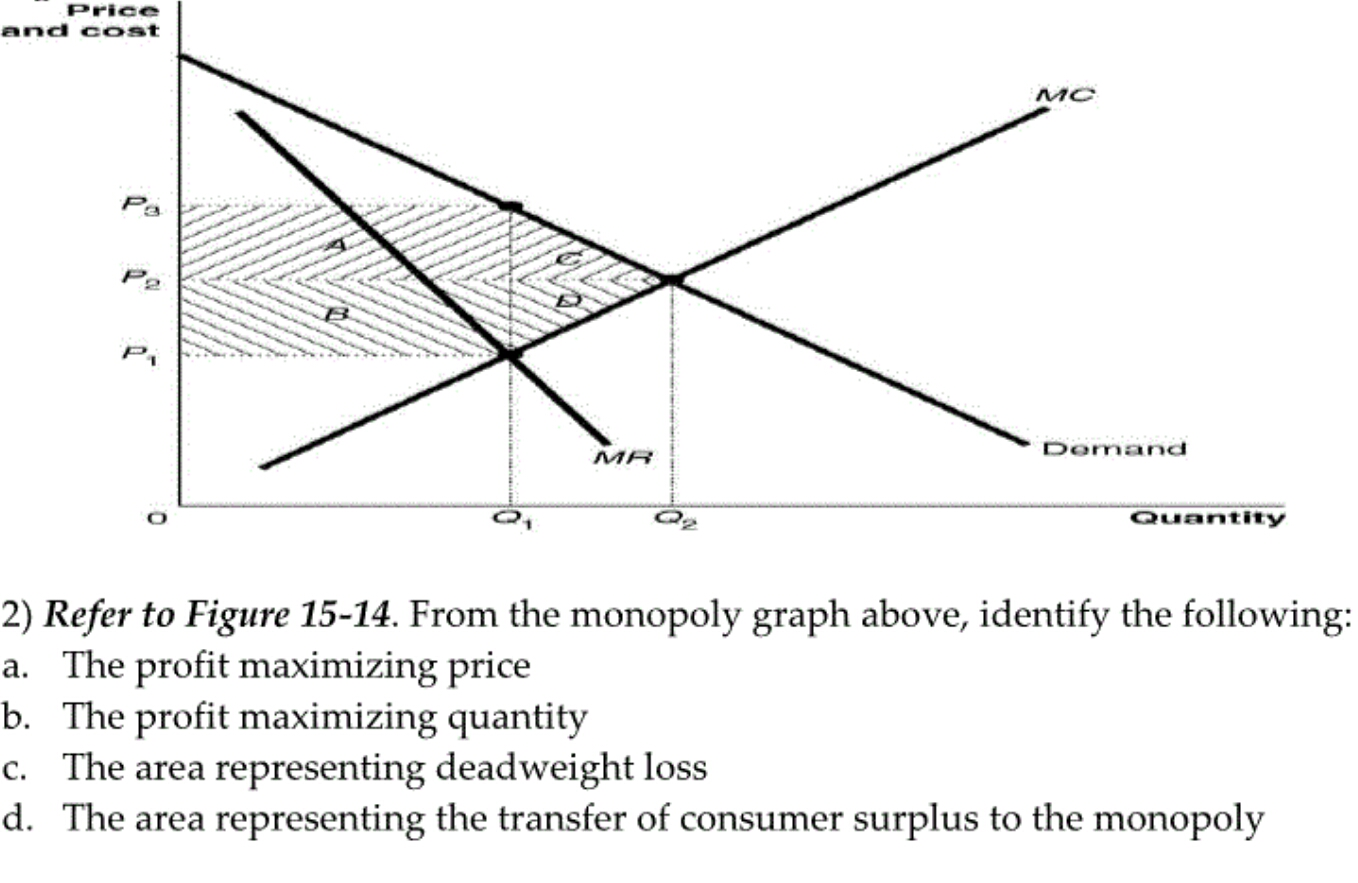 Solved The Profit Maximizing Quantity The Area Represent
Solved The Profit Maximizing Quantity The Area Represent
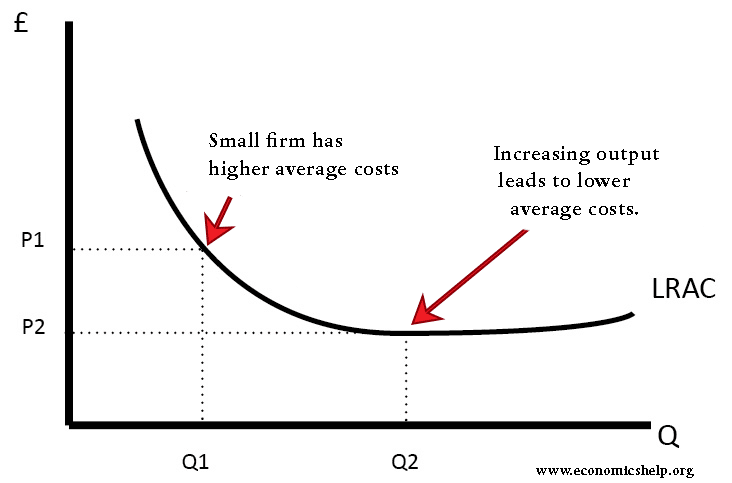 Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help
Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help
 5 1 Externalities Principles Of Microeconomics
5 1 Externalities Principles Of Microeconomics
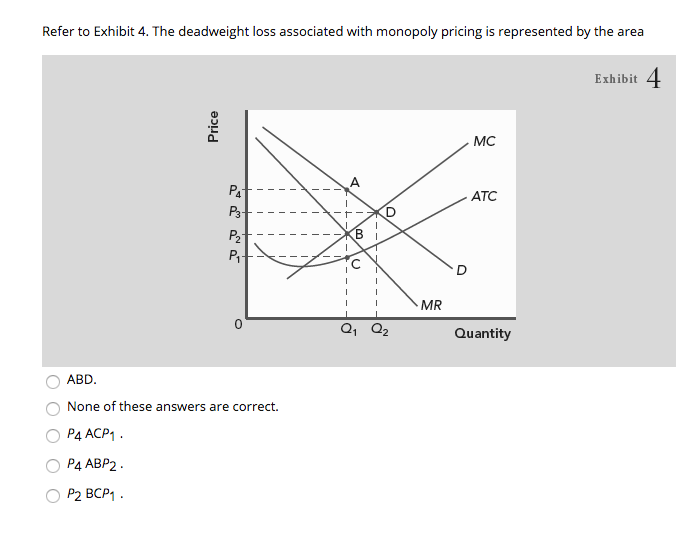 Solved 1 Refer To Exhibit 4 The Deadweight Loss Associ
Solved 1 Refer To Exhibit 4 The Deadweight Loss Associ





0 Response to "Refer To The Diagram To The Right The Deadweight Loss Due To A Monopoly Is Represented By The Area"
Post a Comment